
Why Does the Electric Motor Work Noisy?
We can examine this question in 3 main sources.
1. Magnetic forces: Force the stator package to vibrate in the radial direction.
2. Bearings: Balls and rollers make noise due to geometric structure disorder.
3. Cooling fan: Makes a noise called ventilation noise.
The most effective of these 3 main sources of noise is usually the propeller. This is especially evident in large motors. Special measures can be taken to reduce noise on request. The noise emitted in the air environment is detected in the soundproof and anechoic test room in accordance with DIN EN 21 680-1. The surface sound pressure level (LpfA) in dB (A) is the average of the sound pressure values read on the “A” scale of the sound measuring device, in measurements made at different places at a distance of 1 m from the motor surface. Tolerance +3dB (A).
The noise level in GAMAK electric motors is well below the specified limits.
The values below are valid for 50 Hz mains frequency. For 60 Hz the values increase by about 4dB(A).
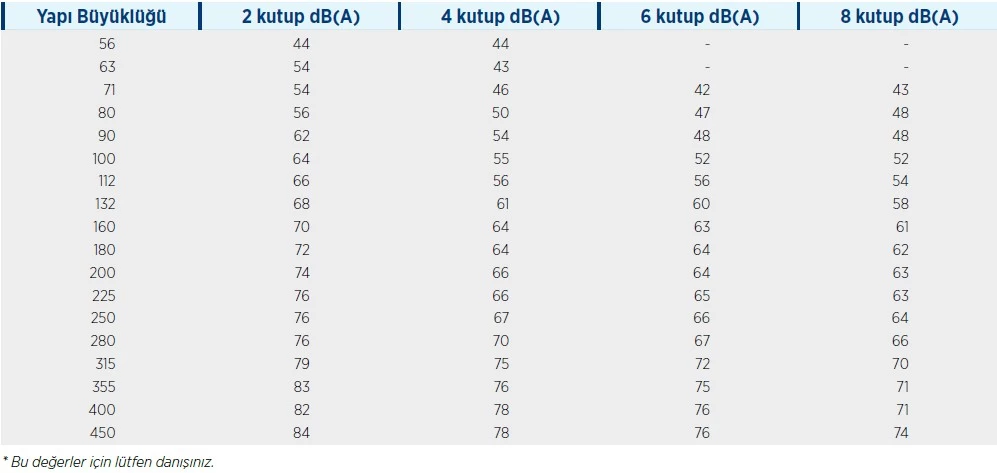
The limits of the noise level in general purpose electric motors are specified in TS EN 60034-9 in the table below.
For detailed information, please contact us.